The History
of Gaumont
1895
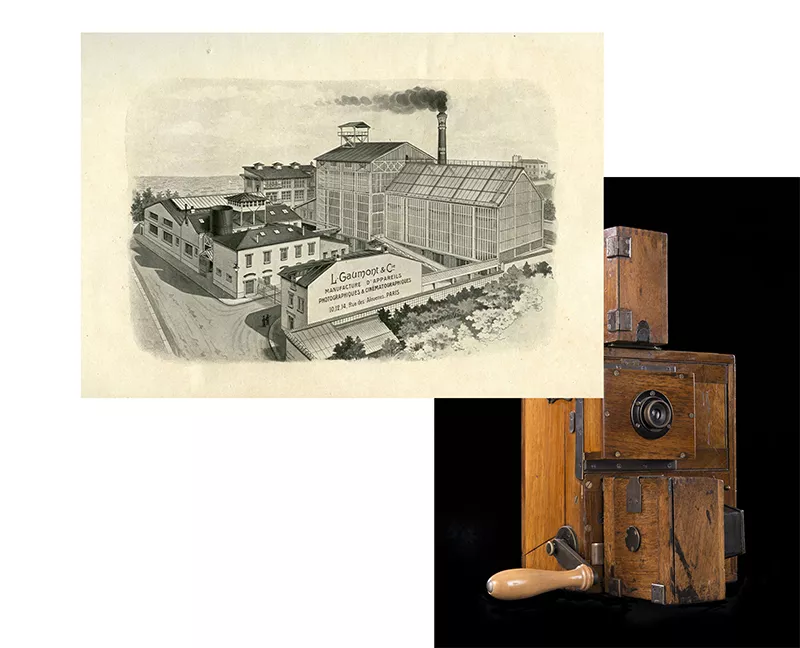
In 1895, when 31-year-old Léon Gaumont took the reins of the Comptoir Général de la Photographie, he never would have suspected that he was going to create the only company in the world that is now as old as cinema itself. The company then sold optical and photographic equipment. Captivated by the work of Edison and the Lumière brothers, Léon Gaumont believed in the future of cinematography and decided to start manufacturing projection equipment in 1900.
Born with cinema

Comedies, dramas,
crime movies,
science fiction, westerns
and even cartoons
Constantly perfecting techniques, he focused especially on the introduction of sound, with the chronophone , and color, with the chronochrome.
Alice Guy, his secretary, quickly suggested (from the late 1890s) enhancing the presentations of equipment sold by the company with filmed sketches.
Soon, titles across all genres were being produced: comedies, dramas, crime movies, science fiction, westerns, and even cartoons created by Émile Cohl, the company's filmmaker.
Later, Louis Feuillade became Gaumont's artistic director, going on to make famous films like JUDEX, FANTÔMAS, and LES VAMPIRES.


1906
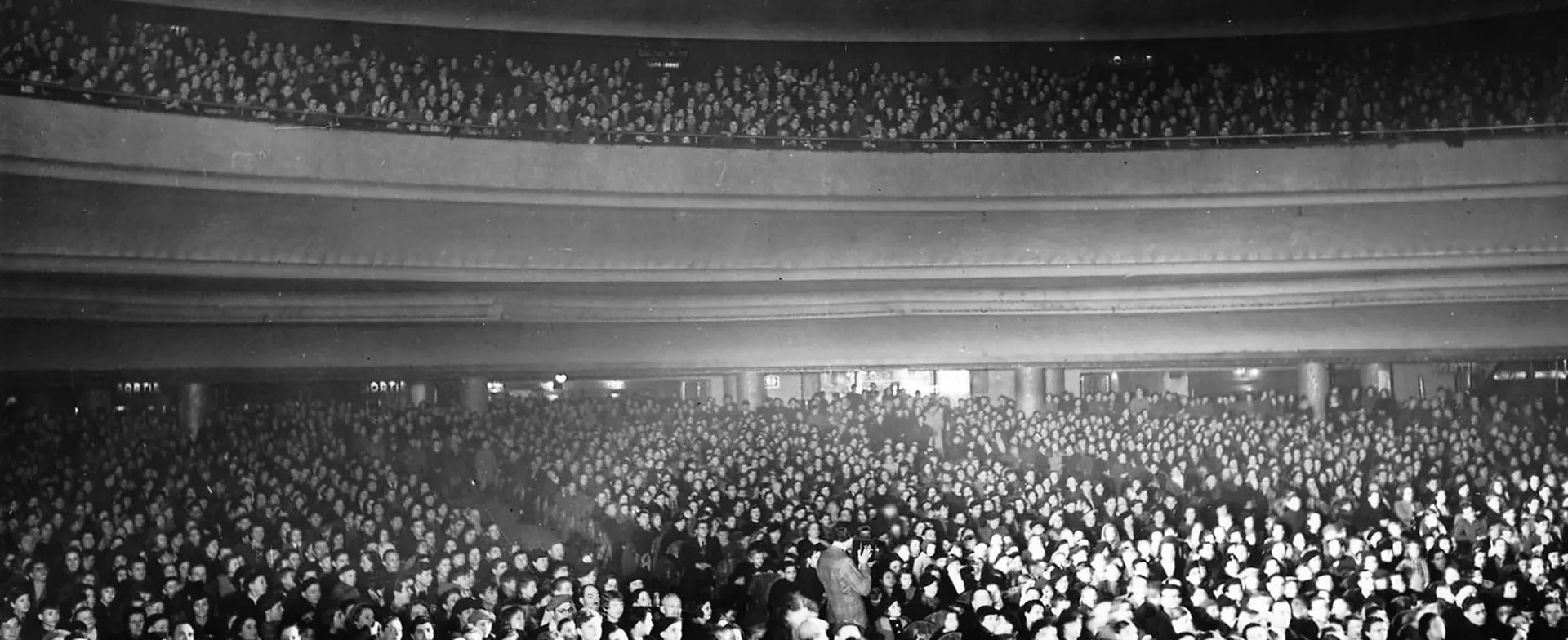
From 1906, and faced with the gradual disappearance of fairground cinema, Gaumont stepped into public film distribution with the opening of its first cinema in Paris.
1907
The arrival of fixed cinemas led tothe introduction of advertising.
So, in 1907, the Imprimerie des Établissements Gaumont was set up, in charge of printing catalogs, bulletins, and posters.
The famous "Gaumont News" was also created in 1910, shown each week in cinemas before the film.
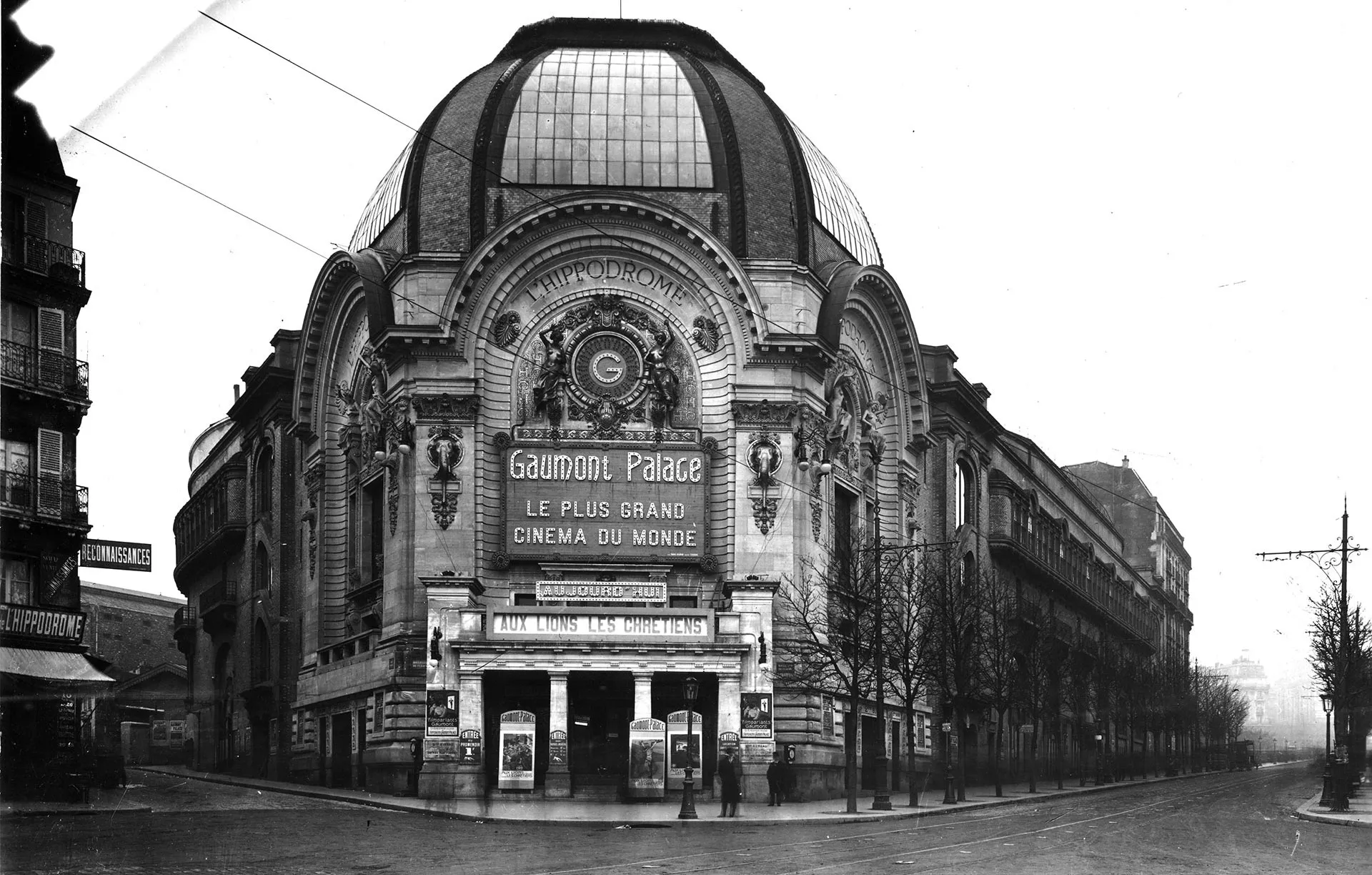

The Gaumont-Palace,
the biggest
cinema in the world
1910
In 1910, Léon Gaumont bought the hippodrome at the Place de Clichy in Paris,
transforming it into a monumental cinema: the Gaumont-Palace, which became —for a time— the biggest cinema in the world.
Gradually setting up cinemas across France,Gaumont became synonymous with an unprecedented mastery of the film production chain, from the manufacture of projection equipment to public distribution.

1925
In 1925, Léon Gaumont signed a distribution agreement with Metro Goldwyn Mayer —a transatlantic first— and created a new company, GMG(Gaumont Metro Goldwyn), which was operational for three years.
Léon Gaumont retired in 1930, with the advent of talking pictures, and a first transformation saw his company become Gaumont Franco Film Aubert (GFFA).
1938
In 1938, GFFA became the Société Nouvelle des Établissements Gaumont (SNEG) with Alain Poiré as secretary-general then director of production and distribution.
Throughout his career, this charismatic man with unrivaled intuition produced or co-produced over 150 feature-length titles,including several cult films.
1975
In 1975, Nicolas Seydoux became the President of Gaumont and injected new momentum
into the company's development, increasing the number of cinemas considerably and committing to an increasingly ambitious approach to production.
Upon his arrival, Daniel Toscan du Plantier imposed a flamboyant style and launched a policy of European production that combined popular hits with avant-garde works.
He also launched the concept of film-opera, most notably with CARMEN by Francesco Rosi and Joseph Losey's DON GIOVANNI. In the mid 80s,Patrice Ledoux produced THE BIG BLUE and THE FIFTH ELEMENT by Luc Besson, as well as Jean-Marie Poiré's JUST VISITING.

2000
In 2000, alongside its production and distribution work, Gaumont joined forces with Pathé to create Cinémas Gaumont Pathé(previously EuroPalaces), thus developing the largest cinema network in Europe.
This partnership lasted until 2017, when Pathé bought back Gaumont's shares.
2003 and 2004
2003 and 2004 saw respectively the creation of Gaumont Video, which made and released DVDs of films from the catalog, and Gaumont Pathé Archives, which brought together the news catalogs of the two founding film companies.
In recent years, Gaumont has heightened its activity, producing,financing, and distributing films in both French and English.
At the same time, with the creation of Gaumont Television in France and around the world, and the acquisition of Gaumont Animation, Gaumont has consolidated its commitment to being present in all audiovisual sectors, developing multi-format and multi-support production.
With its American, British, German, and Italian branches, Gaumont has become a major actor on the international stage, namely producing hits like Narcos, Lupin, Barbarians, and El Presidente.
The company is now directed by Nicolas Seydoux as president, Sidonie Dumas as CEO, and Christophe Riandée as vice CEO.



